design
本项目参考了 ext4fuse 的基本设计和数据结构, 并重新设计了 cache/bitmap/dcache/dentry 部分, 高效的缓存 inode 和 dentry 信息, 大大减少了磁盘读写次数和内存拷贝的操作, 采用高效的指针访问;
同时本项目也实现了
- 文件/目录的创建和删除
- 读写文件
- 权限管理
- 创建硬链接 和 软链接
- 修改访问时间, 修改权限和模式等
static struct fuse_operations e4f_ops = {
.init = op_init,
.getattr = op_getattr,
.access = op_access,
.readdir = op_readdir,
// .releasedir = op_releasedir,
.readlink = op_readlink,
// .mknod = op_mknod,
.mkdir = op_mkdir,
.link = op_link,
.symlink = op_symlink,
.unlink = op_unlink,
.rmdir = op_rmdir,
// .rename = op_rename,
.chmod = op_chmod,
.chown = op_chown,
// .truncate = op_truncate,
.utimens = op_utimens,
.open = op_open,
.flush = op_flush,
// .fsync = op_fsync,
// .release = op_release,
.read = op_read,
.write = op_write,
// .statfs = op_statfs,
.create = op_create,
.destroy = op_destory,
};查找 inode
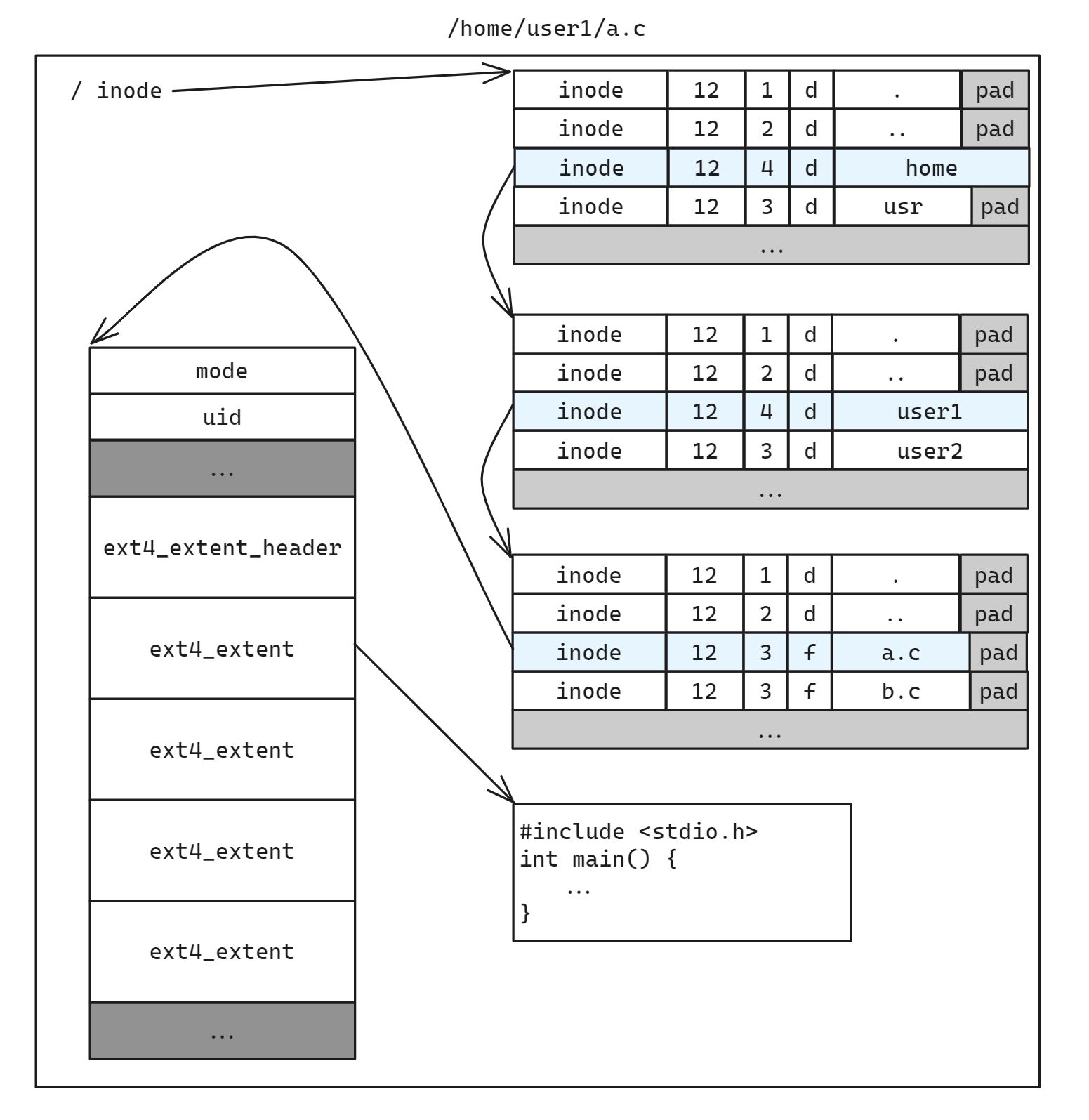
查找 inode 时首先会从 decache 中查找, 如果找不到再依次深入目录遍历目录项, 如果找到了则会将目录项加入到 decache 当中方便下次查找
uint32_t inode_get_idx_by_path(const char *path) {
uint32_t inode_idx = 0;
struct ext4_inode *inode;
DEBUG("Looking up: %s", path);
// first try to find in dcache
struct dcache_entry *dc_entry = get_cached_inode_idx(&path);
inode_idx = dc_entry ? dc_entry->inode_idx : root.inode_idx;
DEBUG("Found inode_idx %d", inode_idx);
do {
uint64_t offset = 0;
struct ext4_dir_entry_2 *de = NULL;
path = skip_trailing_backslash(path);
uint8_t path_len = get_path_token_len(path);
if (path_len == 0) {
// Reached the end of the path
break;
}
// load inode by inode_idx
inode_get_by_number(inode_idx, &inode);
dcache_init(inode, inode_idx);
while ((de = dentry_next(inode, inode_idx, offset))) {
offset += de->rec_len;
if (de->inode_idx == 0 && de->name_len == 0) {
// reach the ext4_dir_entry_tail
ASSERT(((struct ext4_dir_entry_tail *)de)->det_reserved_ft == EXT4_FT_DIR_CSUM);
INFO("reach the last dentry");
de = NULL;
break;
}
INFO("get dentry %s[%d]", de->name, de->inode_idx);
// if length not equal, continue
if (path_len != de->name_len || strncmp(path, de->name, path_len)) {
INFO("not match dentry %s", de->name);
continue;
}
// Found the entry
INFO("Found entry %s, inode %d", de->name, de->inode_idx);
inode_idx = de->inode_idx;
// if the entry is a directory, add it to the cache
INFO("Add dir entry %s:%d to dentry cache", path, path_len);
dc_entry = decache_insert(dc_entry, path, path_len, inode_idx);
break;
}
/* Couldn't find the entry */
if (de == NULL) {
inode_idx = 0;
INFO("Couldn't find entry %s", path);
break;
}
} while ((path = strchr(path, '/')));
return inode_idx;
}高效的 icache
通过 inode_idx 查找 inode 会首先从 icache 中查找, 找不到的话再从磁盘中读取, 并加入 icache 中缓存
int inode_get_by_number(uint32_t inode_idx, struct ext4_inode **inode) {
if (inode_idx == 0) {
return -ENOENT;
}
// first try to find in icache
struct ext4_inode *ic_entry = icache_find(inode_idx);
if (ic_entry) {
DEBUG("Found inode_idx %d in icache", inode_idx);
*inode = ic_entry;
} else {
// inode could not find in icache, read from disk and return the inode
DEBUG("Not found inode_idx %d in icache", inode_idx);
*inode = icache_insert(inode_idx, 1);
}
// update lru count of the inode
ICACHE_LRU_INC(*inode);
return 0;
}其中插入一个新的 icache_entry 后如果已经满了则采用 lru 算法进行替换, icache_entry 设置了 status 位用于标记 INVALID/VALID/DIRTY, 对于比如说 chmod/chown/utimens 这种对于 inode metadata 数据修改的操作, 不必立即写回磁盘; 只需要修改status标记为 DIRTY, 读写都在内存中, 延迟到文件系统释放的时候再将数据同步更新回磁盘
/**
* @brief insert a new inode into icache (LRU if exchange)
*
* @param inode_idx
* @param read_from_disk if false, only register a new inode in i_cache instead of load from disk
useful when inode_create() is called
* @return struct ext4_inode*
*/
struct ext4_inode *icache_insert(uint32_t inode_idx, int read_from_disk) {
if (icache->count == ICACHE_MAX_COUNT) {
INFO("icache is full");
return icache_lru_replace(inode_idx, read_from_disk);
} else {
icache->entries[icache->count].inode_idx = inode_idx;
if (read_from_disk) {
uint64_t off = inode_get_offset(inode_idx);
disk_read(off, sizeof(struct ext4_inode), &icache->entries[icache->count].inode);
}
icache->entries[icache->count].status = ICACHE_S_VALID;
icache->entries[icache->count].lru_count = 0;
icache->count++;
INFO("insert inode %d into icache", inode_idx);
return &icache->entries[icache->count - 1].inode;
}
}索引解析
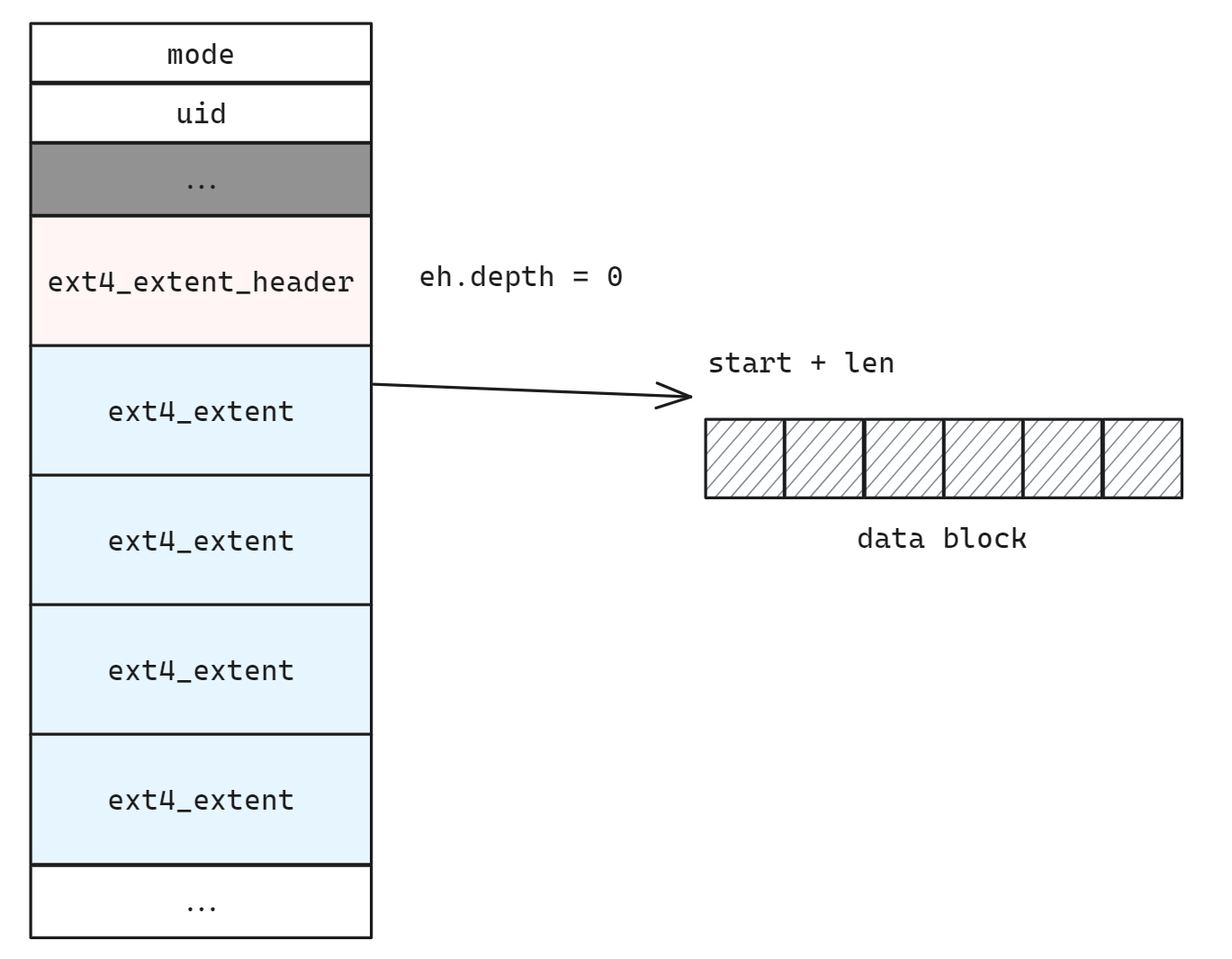
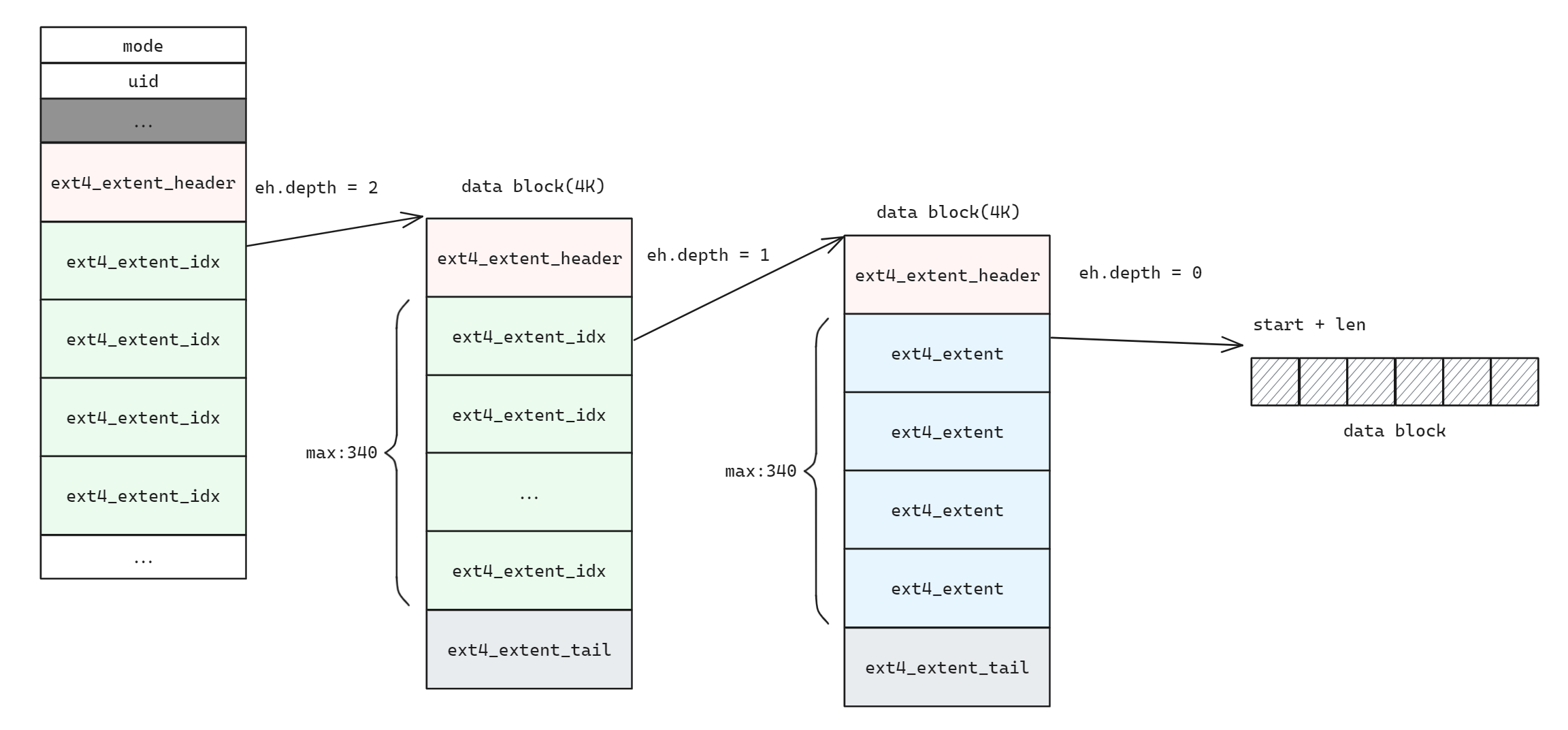
ext4 采用 extent tree 的索引结构, 对于 depth = 0 和 depth > 0 的情况按照 ext4 中介绍的模式递归查找
uint64_t extent_get_pblock(void *extents, uint32_t lblock, uint32_t *len) {
struct ext4_extent_header *eh = extents;
struct ext4_extent *ee_array;
uint64_t ret;
ASSERT(eh->eh_magic == EXT4_EXT_MAGIC);
ASSERT(eh->eh_max <= EXT4_EXT_LEAF_EH_MAX);
DEBUG("reading inode extent, depth = %d", eh->eh_depth);
if (eh->eh_depth == 0) {
// Leaf inode, direct block
// 1 extent header + 4 extents
ee_array = extents + sizeof(struct ext4_extent_header);
ret = extent_get_block_from_ees(ee_array, eh->eh_entries, lblock, len);
} else {
struct ext4_extent_idx *ei_array = extents + sizeof(struct ext4_extent_header);
struct ext4_extent_idx *recurse_ei = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < eh->eh_entries; i++) {
ASSERT(ei_array[i].ei_leaf_hi == 0);
if (ei_array[i].ei_block > lblock) {
break;
}
recurse_ei = &ei_array[i];
}
ASSERT(recurse_ei != NULL);
void *leaf_extents = extent_get_extents_in_block(EXT4_EXT_LEAF_ADDR(recurse_ei));
ret = extent_get_pblock(leaf_extents, lblock, len);
free(leaf_extents);
}
return ret;
}权限管理
代码解析
下面的C函数inode_check_permission根据用户的身份和请求的操作模式,检查并决定是否允许对指定inode(索引节点,代表文件或目录的元数据结构)的访问.
函数参数说明:
inode: 指向EXT4文件系统中inode结构的指针,包含文件的所有权信息(如所有者UID、所属组GID及权限位).
mode: 用户尝试进行的操作模式,定义为READ(只读)、WRITE(只写)、RDWR(读写)、EXEC(执行)中的一个.
typedef enum { READ, WRITE, RDWR, EXEC } access_mode_t;
int inode_check_permission(struct ext4_inode *inode, access_mode_t mode) {
// UNIX permission check
struct fuse_context *cntx = fuse_get_context(); //获取当前用户的上下文
uid_t uid = cntx->uid;
gid_t gid = cntx->gid;
uid_t i_uid = EXT4_INODE_UID(inode);
gid_t i_gid = EXT4_INODE_GID(inode);
DEBUG("check inode & user permission on op mode %d", mode);
DEBUG("inode uid %d, inode gid %d", i_uid, i_gid);
DEBUG("user uid %d, user gid %d", uid, gid);
// allow for root
if (uid == 0) {
INFO("Permission granted");
return 0;
}
// user check
if (i_uid == uid) {
if ((mode == READ && (inode->i_mode & S_IRUSR)) || (mode == WRITE && (inode->i_mode & S_IWUSR)) ||
(mode == RDWR && ((inode->i_mode & S_IRUSR) && (inode->i_mode & S_IWUSR))) ||
(mode == EXEC && (inode->i_mode & S_IXUSR))) {
INFO("Permission granted");
return 0;
}
}
// group check
if (i_gid == gid) {
if ((mode == READ && (inode->i_mode & S_IRGRP)) || (mode == WRITE && (inode->i_mode & S_IWGRP)) ||
(mode == RDWR && ((inode->i_mode & S_IRGRP) && (inode->i_mode & S_IWGRP))) ||
(mode == EXEC && (inode->i_mode & S_IXGRP))) {
INFO("Permission granted");
return 0;
}
} else {
// other check
if ((mode == READ && (inode->i_mode & S_IROTH)) || (mode == WRITE && (inode->i_mode & S_IWOTH)) ||
(mode == RDWR && ((inode->i_mode & S_IROTH) && (inode->i_mode & S_IWOTH))) ||
(mode == EXEC && (inode->i_mode & S_IXOTH))) {
INFO("Permission granted");
return 0;
}
}
INFO("Permission denied");
return -EACCES;
}功能说明
(1)获取用户上下文
使用fuse_get_context()获取当前发起操作的用户上下文,包括用户ID(uid)和组ID(gid).
- id:是一个命令行工具,用于显示当前用户的身份号码,包括用户ID(UID)和组ID(GID).在FUSE文件系统中,这些身份号码通常用于权限检查.
- uid:用户身份号码
- gid:某用户所属的用户组号码,该用户加入用户组后就拥有了这些用户组成员共同拥有的权限.
struct fuse_context *ctx = fuse_get_context();
uid_t uid = ctx->uid; //用户ID
gid_t gid = ctx->gid; //组ID(2)inode权限检查
- 在执行任何文件操作之前,需要先检查当前用户的身份是否有权限执行该操作,通常在每个文件操作的回调函数中完成.
- 在FUSE中,inode通常包含有关文件权限的信息.我们需要实现一个函数来检查给定用户是否有权限访问inode.
①超级用户检查
命令行工具su和sudo常用来切换超级用户.
- su(替代用户)允许用户以另一个用户的身份运行shell.通常用于切换到root用户或其他具有更高权限的用户.
- sudo(超级用户执行)允许授权的用户以另一个用户(通常是root)的身份执行命令,而无需共享root密码.
如果当前用户是root(uid == 0),由于root具有系统最高权限,直接允许所有操作.
②所有者权限检查
比较inode的所有者UID与当前用户的UID.如果匹配且请求的操作模式与inode权限位(如S_IRUSR读权限、S_IWUSR写权限)相符合,则允许访问.
③组用户权限检查
如果inode的所属组GID与当前用户所在的组GID相同,且权限位(如S_IRGRP、S_IWGRP)满足请求的操作模式,则权限被授予.
④其他用户权限检查
除了uid和gid外,还要检查其他用户
最后,检查inode针对"其他人"的权限位(如S_IROTH、S_IWOTH).如果这些权限位允许请求的操作,则访问被许可.
⑤权限拒绝处理
如果以上所有条件都不满足,则通过返回-EACCES错误码,表明访问被拒绝.
(3)更改权限和所有权
我们还可以实现op_chmod和op_chown等操作来允许用户更改文件权限和所有权.
op_chmod更改文件权限
更改文件的权限有两种表示方法,一种是用数字表示权限,另一种是用 rwx 表示权限.为了说明怎么用数字表示权限,我们得先来了解一下八进制.chmod 代表"更改模式"(change mode),是一个用于更改文件或目录权限的命令行工具.它允许用户设置读(r)、写(w)和执行(x)权限.
op_chown更改文件所有者
chown是一个命令行工具,用于更改文件或目录的所有者.这通常需要管理员权限.
chgrp:是一个更改组的命令行工具,用于更改文件或目录的组所有权.与chown类似,这通常需要管理员权限.
为了使权限检查功能完备,我们需要在inode_check_permission函数中加入实际的权限验证代码.这通常涉及以下步骤:
- 权限掩码比对:利用inode中的权限位(如读权限为4,写权限为2,执行权限为1)与用户身份进行比对.对于文件所有者、同组用户、其他用户分别有不同的权限设定.
- 特殊权限处理:考虑SUID、SGID、sticky bit等特殊权限标志的影响.
- 错误处理:当权限检查不通过时,应当有明确的错误处理逻辑,例如返回非零值表示权限拒绝.